Radiation, a phenomenon commonly encountered in our daily lives, is a complex and diverse subject that requires a meticulous understanding. In this article, we will delve into the various types of radiation, explore its sources lead door, and examine the electromagnetic spectrum.
Furthermore, we will discuss the potential health effects of radiation exposure and provide valuable insights on how to protect ourselves from its adverse consequences. Through this technical and detail-oriented exploration, we aim to equip our freedom-seeking audience with the knowledge they seek regarding the enigma of radiation.

The Different Types of Radiation
Ionizing radiation, such as gamma rays and X-rays, and non-ionizing radiation, like radio waves and microwaves, are the two main types of radiation.
Ionizing radiation consists of high-energy particles that have the ability to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms Lead brick, leading to the formation of charged particles called ions. This type of radiation is commonly used in radiation therapy, a medical treatment that uses high doses of ionizing radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors.
On the other hand, non-ionizing radiation has lower energy levels and does not have enough energy to remove electrons from atoms. It is commonly used in various applications such as communication technologies, including radio waves for broadcasting and microwaves for cooking. Additionally, non-ionizing radiation is also utilized in medical diagnostics, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Furthermore, ionizing radiation plays a crucial role in nuclear power, where it is used to generate electricity through controlled nuclear reactions.
Both types of radiation have different properties and applications, and understanding their characteristics is essential for various fields including healthcare, telecommunications, and energy production.
Sources of Radiation
One of the primary sources of radiation exposure for humans is through medical imaging procedures such as X-rays and CT scans. These procedures involve the use of ionizing radiation to produce images of the body’s internal structures. While the benefits of medical imaging are undeniable, it is important to recognize that excessive exposure to radiation can have detrimental effects on human health.
Apart from medical imaging, other sources of radiation exposure include nuclear disasters and radiation therapy. Nuclear disasters, such as the Chernobyl and Fukushima accidents, release large amounts of radioactive isotopes into the environment, leading to widespread radiation exposure.
On the other hand, radiation therapy is a medical treatment that uses high doses of radiation to target and destroy cancer cells. While the benefits of radiation therapy are significant, it is crucial to carefully manage and monitor the radiation doses to minimize potential harm to the patients.
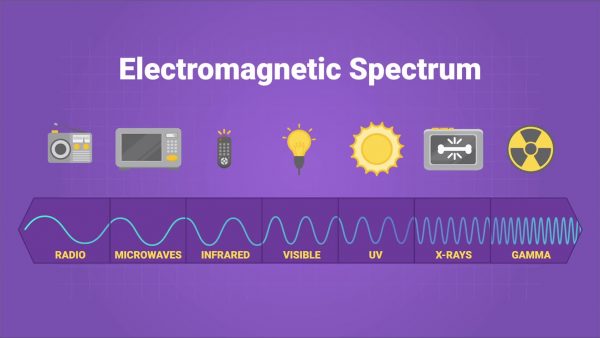
Understanding the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is a range of electromagnetic waves with varying frequencies and wavelengths that include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. This spectrum plays a crucial role in our daily lives, with numerous applications that we often take for granted.
For example, radio waves are used in broadcasting and communication systems, allowing us to listen to music, news, and talk shows. Microwaves are used in cooking and heating food, while infrared waves are used in remote controls and thermal imaging. Visible light allows us to see the world around us, while ultraviolet waves are used in sterilization and tanning. X-rays and gamma rays have applications in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
Additionally, the electromagnetic spectrum is the foundation of communication technology, as it enables the transmission of signals through various devices such as radios, televisions, cell phones, and satellite communication systems. These devices use different wavelengths and frequencies to transmit and receive information, allowing us to stay connected with others around the world.
Potential Health Effects of Radiation Exposure
Exposure to radiation from the electromagnetic spectrum can have potential health effects that need to be carefully studied and understood.
Long-term effects of radiation exposure are a subject of concern, especially in the field of radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is a widely used treatment for cancer, where high-energy radiation is directed at cancerous cells to destroy them. While this treatment can be effective in targeting and killing cancer cells, it can also affect healthy tissues and organs in the vicinity.
The long-term effects of radiation therapy can include damage to DNA, leading to genetic mutations and an increased risk of developing secondary cancers. Additionally, radiation therapy can cause inflammation, fibrosis, and scarring in the treated area, which can result in long-lasting complications.
Therefore, it is essential to carefully monitor and manage the potential long-term effects of radiation therapy to ensure the well-being of patients.
Protecting Ourselves From Radiation
To effectively minimize the risks associated with radiation, it is crucial to implement comprehensive safety measures and protocols. Radiation shielding is one such measure that can help protect individuals from the harmful effects of radiation exposure. Shielding involves the use of materials, such as lead or concrete, to block or absorb radiation.
The effectiveness of shielding depends on factors such as the type and energy of radiation, as well as the thickness and composition of the shielding material. Additionally, radiation detection plays a vital role in protecting against radiation. Radiation detectors, such as Geiger-Muller counters or scintillation detectors, are used to measure and monitor radiation levels in various environments. These devices provide real-time information about radiation levels, allowing individuals to take necessary precautions and ensure their safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, radiation refers to the emission of energy in the form of waves or particles. It can be classified into ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, with various sources such as nuclear power plants, X-rays, and the Sun.
Understanding the electromagnetic spectrum helps us comprehend the different types of radiation and their potential health effects.
To protect ourselves from radiation exposure, proper safety measures and precautions should be taken.
Overall, a thorough understanding of radiation is crucial in order to mitigate its potential risks.
…